++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ 删除一个字段的unique key create table t2(id int unique key);不能直接去修改列的类型,因为这是一种索引约束。
alter table t2 drop index id;
create table t3(id int primary key not null auto_increment,name varchar(20)); #单个字段为主键 create table t4(id int not null auto_increment,name varchar(20),primary key (id,name));#多个字段为主键 +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ 1、DQL介绍 select--------- 主要针对数据内容查看 show------- 主要针对原数据查看,属性类。 2、select 语句的应用 2.1、select 单独使用 select @@port; select @@basedir; #系统参数 select database(); # 查询自己在那个库下面,相当于linux 的 pwd select now(); #查询当前时间 2.2、select 通用语法(单表) ***** select 列 from 表 where 条件 group by 条件 having 条件 order by 条件 limit 2.3、学习环境数据库world说明 http://www.xchinagroup.top/softdown/centos7/03_mysql/world.sql http://www.xchinagroup.top/softdown/centos7/03_mysql/school.sql

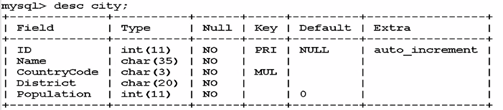
2.4、select 配合 from 子名使用 ---- select 列,列,列 from 表 查询表中所有的信息(生产中几乎是没有这种需求的) select id,name,countrycode,district,population from city; 或者 select * from city; 查询表中name 和 population 的值 select name,population from ctiy; 2.5、select 配合 where 子句使用 ----- where 等值条件查询 例子:查询中国所有的城市名和人员数 select name,population from city where countrycode='CHN'; ---- where 配合比较判断查询(> < >= <=) 例子:查询世界上小于100人的城市名和人口数 select name,population from city where population<100; ---- where 配合 逻辑连接符( and or) 例子:查询中国人口数量大于800w的城市名和人口数 select name,population from city where countrycode='CHN' and population>8000000; 查询中国或美国的城市名和人口数 select name,population from city where countrycode='CHN' or countrycode='USA'; 查询世界上人口数量在500w 到 600w 之间的城市名和人口数 select name,population from city where population>5000000 and population<6000000; select name,population from city where population between 5000000 and 6000000; +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ---- where 配合 like 子句 模糊查询 例子:查询countrycode 中有CH开关的城市信息 select * from city where countrycode like ' CH%'; # % 表示所有 注意:like 模糊查询,不要出现类似于('%CH%'),前后都有%的语句,会严重影响系统性能,因为不走索引。 如果业务中有大量这样的需求,我们用ES---elasticsearch 来代替 --- where 配合 in 语句 查询中国或者美国的城市信息 select name,population from where in ('CHN','USA'); #等同于 or 条件查询 +++++++++++ select 配合 group by + 聚合函数 常用聚合函数:max(),min(),avg(),count(),sum() group by 功能:将某列中有共同条件的数据行,分成一组,再进行聚合函数操作。 例子:统计世界上每个国家的城市个数 select countrycode,count(id) from city group by countrycode; 统计每个国家的总人口数 select countrycode,sum(population) from city group by countrycode; 统计每个国家 省 的个数 select countrycode,sum(distinct population) from city group by countrycode;#distinct 去除重复数据 统计中国 每个省的总人口数 select district,sum(population) from city where countrycode='CHN' group by district; 统计中国 每个省城市的个数 select district,count(id) from city where countrycode='CHN' group by district; 扩展:统计中国 每个省城市的名字列表 类似于 guangdong guangzhou,shenzhen,foshan,....,..... 显示 select district,group_concat(name) from city where countrycode='CHN' group by district;
将上述结果,拼结成一行显示,用冒号分隔,类似于 Anhui: heifei,huaian,....,.... select concat(district,": ",group_concat(name)) from city where countrycode='CHN' group by district;
concat() 拼结函数,将字符串拼结在一起。 2.6、+++++++++++ select 配合 having 应用 例子:统计所有国家的总人口数量,将总人口数大于1亿的过滤出来。 select countrycode,sum(population) from city group by countrycode having sum(population)>100000000; having 不走索引,可以理解为走的全表,如果前面求出的结果集比较大的话,性能还是会有影响。 2.7、+++++++++++ select 配合 orderby 子句 对结果集进行排序,可以单独使用。 例子:统计所有国家的总人口数,将总人口数大于5000w的过滤出来,从大到小排序。 select countrycode,sum(population) from city group by countrycode having sum(population)>50000000 order by sum(population) desc; 2.8、+++++++++ select 配合 limit 子句 例子:统计所有国家的总人口数量,将总人口数大于5000w的过滤出来,从大到小排序。显示前三名。 select countrycode,sum(population) from city group by countrycode having sum(population)>50000000 order by sum(population) desc limit 3; 例子:统计所有国家的总人口数量,将总人口数大于5000w的过滤出来,从大到小排序。显示前4-6名。 select countrycode,sum(population) from city group by countrycode having sum(population)>50000000 order by sum(population) desc limit 3,3; ### limit 3,3 跳过第3行,显示一共3行,相当于从第4 行开始,总共显示3行,就是,4,5,6 ### limit 3 offset 3(跳过offset 后面的3行,显示一共limit 后面的3行) 等同于 limit 3,3
limit 3 也等同于 limit 3 offiset 0 2.9、union 和 union all 作用:多个结果集,合并查询的功能。 ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ 例子:查询中国或者美国的城市信息 select * from city where countrycode='CHN' or countrycode='USA'; 改写为:union all ,性能比or 这种要好很多,因为改写后的语句,它的索引等级高一些。 select * from city where countrycode='CHN' union all select * from city where countrycode='USA'; 面试题:union 和 union all 的区别: union all 不做去重,生产中用得多一些。 union 会做去重,就会涉及到做排序计算等,性能没有union all 好。 3、多表连接查询(内连接) 3.1、作用:单表数据不能满足查询需求时。 3.2、多表连接查询,基本语法 最核心的是,找到多张表之间的关联条件列 列书写时,必须是:表名.列 所有涉及到的查询列,都放在select 后 将所有的过滤,分组,排序等条件按顺序写在on 的后面 例子:查询世界上小于100人的城市,所在的国家名,国土面积,城市名,人口数 select country.name,country.surfacearea,city.name,city.name,city.population from city join country on city.countrycode=country.code where city.population<100; +++++++++++++++++++++++++ 多张表连接: a join b on a.x=by.y join c on b.m=c.n ### join 和 on 是配对使用的,先 a join b 然后再 b join c
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ 3.3、多表连接例子: 统计zhang3,学习了几门课 select student.sname,count(score.sno) from student join score on student.sno=score.sno where student.sname='zhang3'; 查询 zhang3 学习了的所有的课程的分数。 select student.sname,course.cname,score.score from student join score on student.sno=score.sno join course on score.cno=course.cno where student.sname='zhang3';
-- 查询 zhang3 学习的所有课程的分数显示一行。 SELECT student.sname,GROUP_CONCAT(CONCAT(course.cname,": ",score.score)) FROM student JOIN score ON student.sno=score.sno JOIN course ON score.cno=course.cno WHERE student.sname='zhang3' GROUP BY student.sname;
SELECT CONCAT(student.sname,": ",GROUP_CONCAT(CONCAT(course.cname,": ",score.score))) FROM student JOIN score ON student.sno=score.sno JOIN course ON score.cno=course.cno WHERE student.sname='zhang3' GROUP BY student.sname;
查询zhang3,学习的课程名称有那些? select student.sname,course.cname from student join score on student.sno=score.sno join course on score.cno=course.cno where student.sname='zhang3';
-- 查询zhang3 学习的课程名称有那些,并显示为一行: select student.sname,group_concat(course.cname) from student join score on student.sno=score.sno join course on score.cno=course.cno where student.sname='zhang3' group by student.sname;
select concat(student.sname, ": ",group_concat(course.cname)) from student join score on student.sno=score.sno join course on score.cno=course.cno where student.sname='zhang3' group by student.sname;
查询oldguo 老师教的学生名和个数 select teacher.tname,group_concat(student.sname),count(student.sname) from teacher join course on teacher.tno=course.tno join score on course.cno=score.cno join student on score.sno=student.sno where teacher.tname='oldguo' group by teacher.tno;
查询oldguo教师所教课程的平均分数 select teacher.tname,avg(score.score) from teacher join course on teacher.tno=course.tno join score on course.cno=score.cno where teacher.tname='oldguo' group by score.cno;
每位老师所教课程的平均分,并按平均分排序 select teacher.tname,avg(score.score) from teacher join course on teacher.tno=course.tno join score on course.cno=score.cno group by teacher.tname,score.cno order by avg(score.score);
查询oldguo所教的不及格的学生姓名 select teacher.tname,student.sname,score.score from student join score on student.sno=score.sno join course on score.cno=course.cno join teacher on course.tno=teacher.tno where score.score<60 and teacher.tname='oldguo';
查询所有老师所教学生不及格的信息 select teacher.tname,student.sname,score.score from student join score on student.sno=score.sno join course on score.cno=course.cno join teacher on course.tno=teacher.tno where score.score<60;
select teacher.tname,group_concat(concat(student.sname,": ",score.score)) from teacher join course on teacher.tno=course.tno join score on course.cno=score.cno join student on score.sno=student.sno where score.score<60 group by teacher.tno;
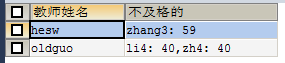
3.4、别名应用: 表别名:----->全局都可以调用 select teacher.tname,group_concat(concat(student.sname,": ",score.score)) from teacher join course on teacher.tno=course.tno join score on course.cno=score.cno join student on score.sno=student.sno where score.score<60 group by teacher.tno; +++++++++++ select t.tname,group_concat(concat(st.sname,": ",s.score)) from teacher as t join course as c on t.tno=c.tno join score as s on c.cno=s.cno join student as st on s.sno=st.sno where s.score<60 group by t.tno;
列别名:-----> 只能被 having 和 order by 调用 select t.tname as 教师姓名,group_concat(concat(st.sname,": ",s.score)) as 不及格的 from teacher as t join course as c on t.tno=c.tno join score as s on c.cno=s.cno join student as st on s.sno=st.sno where s.score<60 group by t.tno;